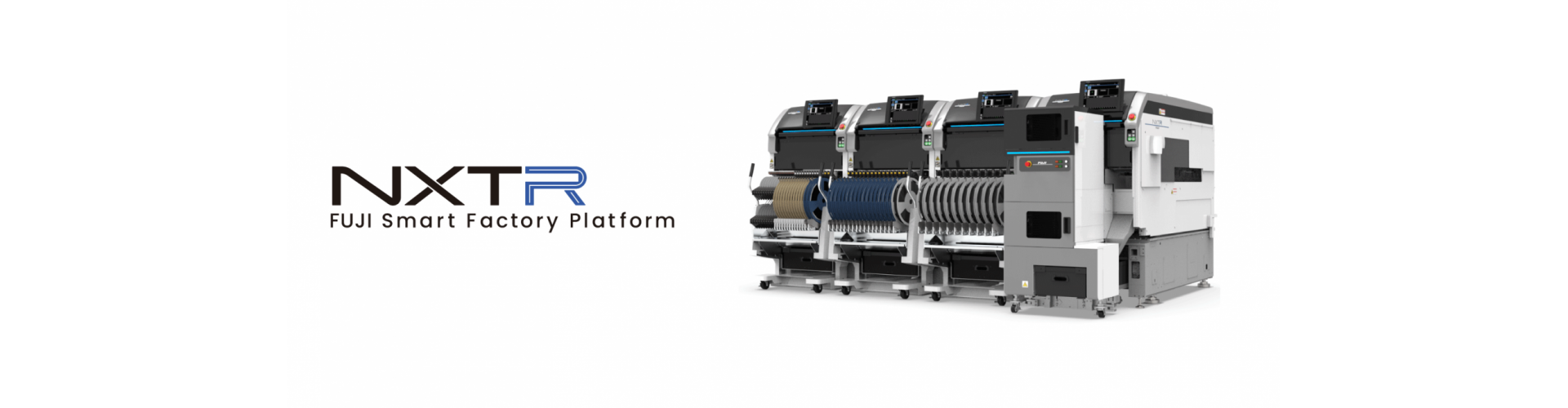
The NXTR S model offers a truly modular design for the optimal line configuration that caters to your production.
Real-time sensing placement, optimized placement actions, and part handling checks after placement are just a few examples.
This high-end model machine from the NXT series supports new functions that preserve a high level of QCD performance.
Fuji is paving the way to the future of Smart Factories with NXTR.
Product Features
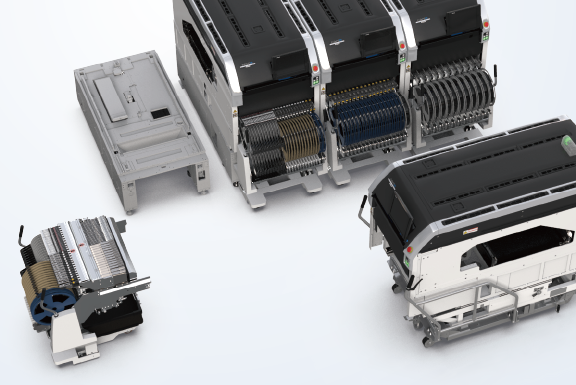
This machine continues the concept of true modularity from the NXT series.
This true modularity is a unique feature to Fuji and none of our competitors can match it.

Fuji's original compact lightweight heads can be easily exchanged without using tools.
This allows operators to perform maintenance and troubleshoot unexpected problems.

The quantity of robots per module and types of heads used can be selected to match your product, giving you the optimal production equipment.
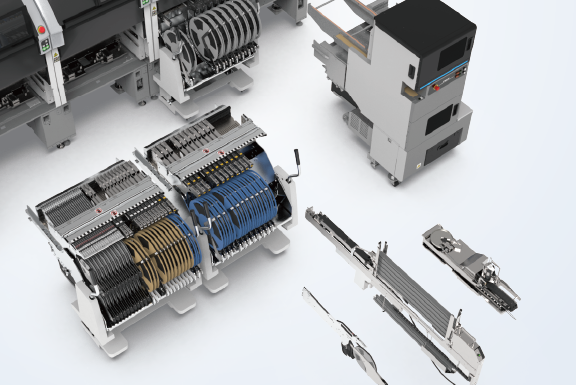
You can select the optimum supply units to match the production type and parts used.
Feeders and other supply devices from other Fuji products you may have can also be used, encouraging efficient use of the units in your assets.
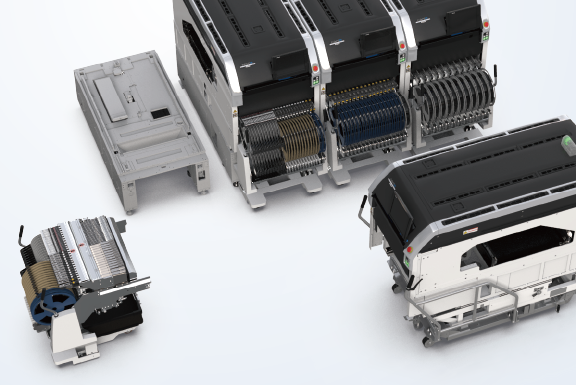
Additional investment can be made on the scale of single modules.
You can gradually increase the production capacity to the necessary extent with minimal investment for each.

The modules are designed for single side operation that streamlines and optimizes the operation traffic.
This increases efficiency in supplying materials and performing maintenance work.

Nozzles, feeders, and also heads are applicable for offline maintenance.
Using automation units ensures reliable maintenance without requiring any skills.
Linking these units with Nexim improves maintenance management.
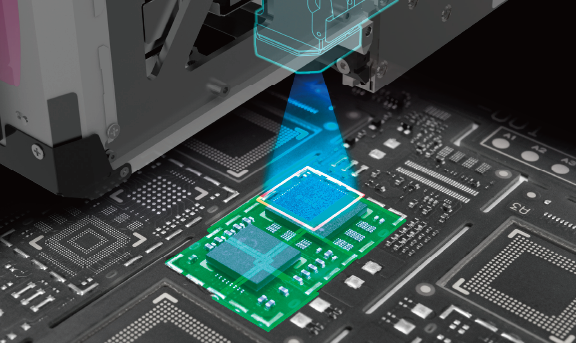
Maintaining a high level of quality on all placements
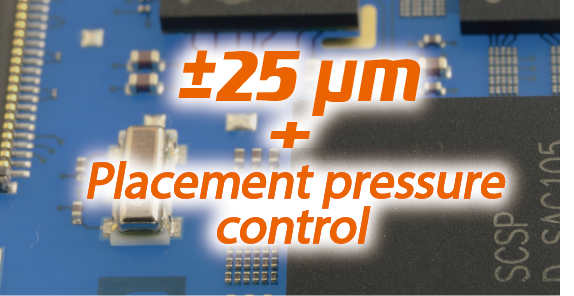
Placements can be performed with a high accuracy of ±25 µm at all times; there are no constraints for the head type or the part to be placed.
Additionally, controlling the push-in amount during placement allows for placement with the appropriate pressure.
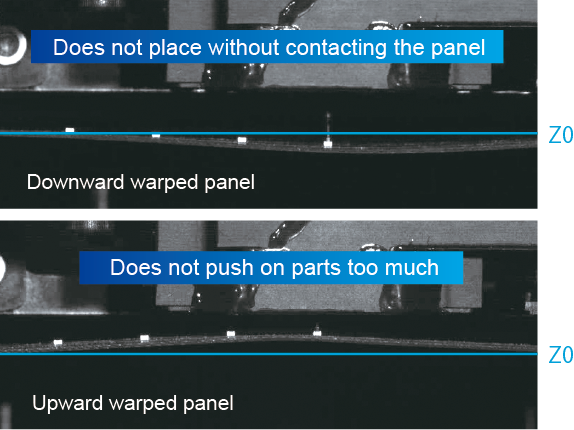
Adjusting the placement height
The placement stroke follows changes in the placement height due to panel warpage and distortions, which allows the machine to control the appropriate push-in amount and moreover prevents placement deviations and excess stress on parts and panels.
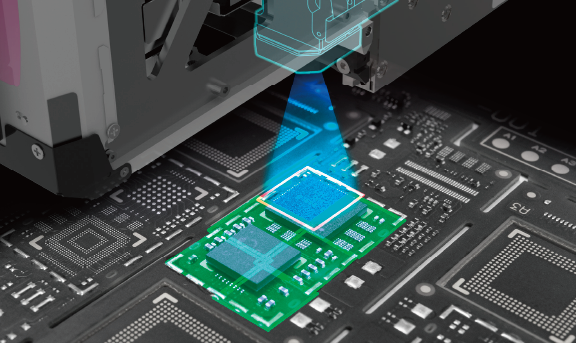
Mark and parts inspection (MPI)
Various checks are available within placement machines to verify the process result shortly after that process: Checking placement immediately following placement, and checking placed parts before placing shield parts, for example.
This prevents production of defective products and reduces wasted time and parts.
(Under development)
- Part presence check
- Misaligned placement check
Intelligent parts sensor (IPS)
The installed IPS system can cater to a wide range of checks, from part pickup stance to parts remaining on nozzles, as well as upside-down checks for minimold parts.
It prevents placement defects attributed to packaging, nozzles, and parts.
- Check for dropped parts
- Check of the part height
- Check for parts presence
- Check for parts remaining on nozzle
- Check for stuck nozzles
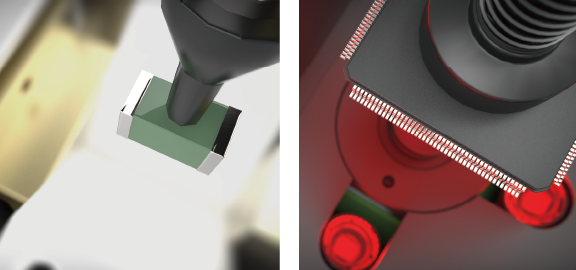
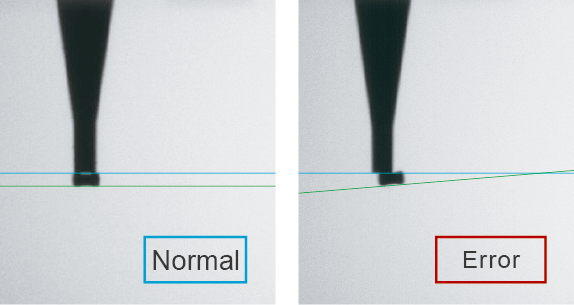
LCR check, 3D coplanarity check
Placement defects caused by operation errors and defective parts are prevented by checking the electrical properties of chip parts with LCR checks and by checking the leads and bumps on IC parts with coplanarity checks. (Option)
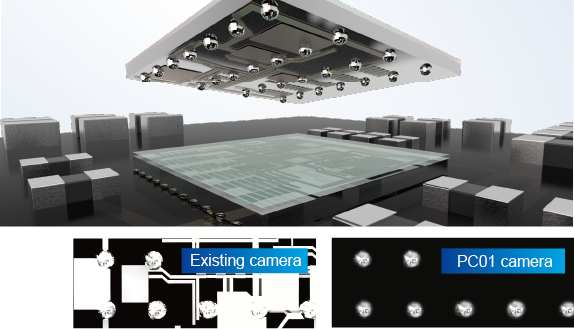
The camera, equipped with advanced lighting technology, ensures vision processing of WL-CSPs and other parts for which the structural context of parts are likely captured in the acquired images.
This results in high accuracy placement.
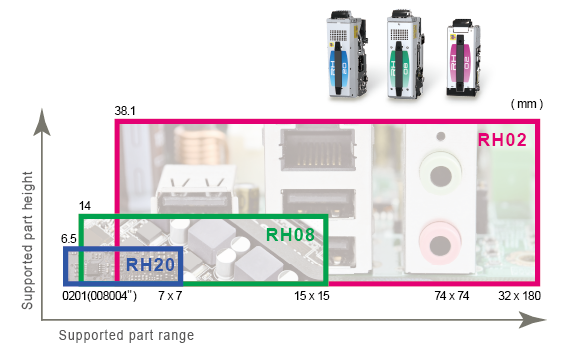
Building production lines with the flexibility to handle various types of production.
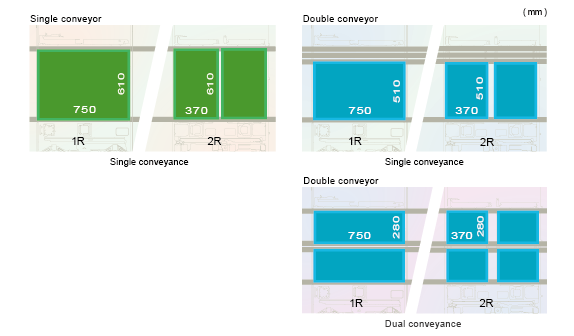
The panel size coverage is expanded so that panels up to 750 x 610 mm are supported "with single conveyors" and up to 370 x 280 mm "with double conveyors" when using dual lane production.
From large panel production to highly-efficient production of producing panels in the same size, NXTR line configurations are capable of supporting a greater variety of production.
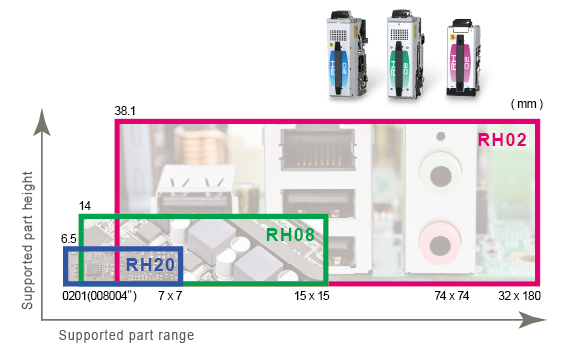
The three newly-developed heads are capable of handling an expanded part range.
They contribute to line balancing and flexible production without drops in production rates even when a different set of parts is used in the next production.
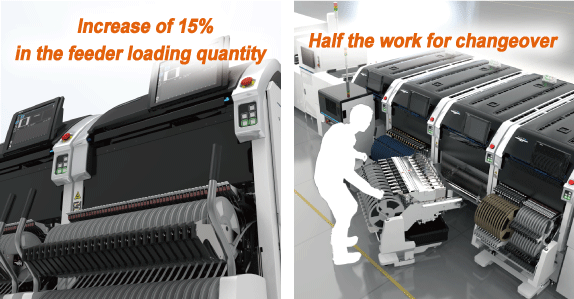
Increase of 15% more feeders can be set versus previous machines.
In addition, the feeder changeover work can be reduced by half with batch feeder exchange because an MFU unit is used for the parts supply unit.
This contributes to improved machine availability.
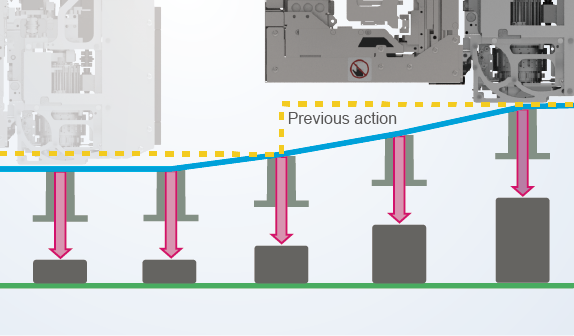
Operation can be optimized in various ways to suit the part being placed, such as by selecting stable and optimal operation speeds and streamlining Z direction strokes in view of the part height.
In addition to making it possible to support various parts, this also improves cycle time as well.
- Multi-level transfer speed
- Shortest Z stroke control

The appropriate hard-type or soft-type backup pins are allocated automatically.
This function is an effective measure to reduce work and prevent mistakes during changeover. (Option)
- Program-based positioning
- Auto allocation position check
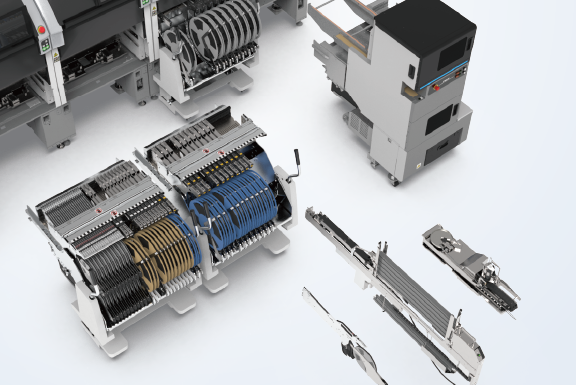
Responding to evolving parts and production models, and advancing total line efficiency
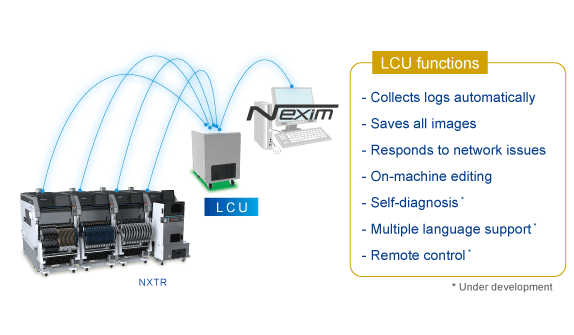
By automatically saving logs and image data, signs of issues that would cause machine stops and information that would lead to problem solving is not missed, leading to faster recovery times.
Network conditions are monitored constantly, which prevents production stops associated with network issues from occurring.
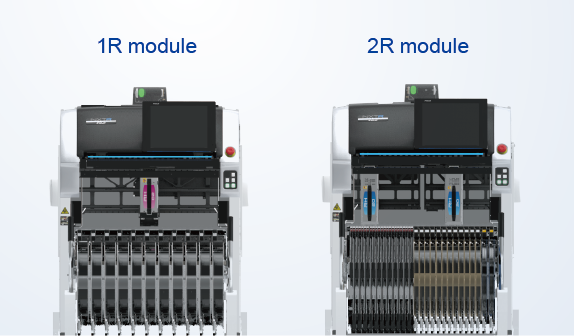
The most appropriate modules can be selected from the two module types based on the panel size and quantity of feeders to set.
It is possible to change modules after the line has been set up.

Pulling forward the module opens up access to the inside the machine with ease from both sides.
This makes it possible to exchange heads and other units and perform maintenance work with a comfortable posture.

The high-speed type dip flux unit transfers flux onto the bumps of small parts. This leads to high-speed placement. (Option)

